43 how do ocean currents work
How Does Tidal Power Work? - Solar Reviews Tidal energy is a form of hydropower that works by harnessing the kinetic energy created from the rise and fall of ocean tides and currents, also called tidal flows, and turns it into usable electricity. The larger the tidal range, or the height difference between sea level at high and low tide, the more power can be produced. Deep Diving for Metals: Visualizing How Ocean Mining Works Source: The Metals Company. The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) has so far approved 28 exploration contracts in the Pacific, Indian and Atlantic Oceans, covering 1.3 million square kilometers of the ocean floor.. With many companies turning their eyes to the unexplored riches of the ocean, seabed mining could offer a wealth of untapped minerals on the ocean floor.
How do Flying Fish "Fly"? - Ocean Conservancy But they do use their very large pectoral, or side, fins to glide over the ocean surface. First, they swim very fast under water, reaching speeds of more than 35 miles per hour. Then, they use this momentum to launch themselves out of the water and fan their fins out to glide forward. Flying fish can "fly" for up to 650 feet—that's over ...

How do ocean currents work
How does OTEC work? (ocean thermal energy conversion ... How does it work? First, the pipe flows through a heat exchanger fixed in the hot surface waters of the ocean, which makes the ammonia boil and vaporize. The heated ammonia vapor expands and blows through a turbine, which extracts some of its energy, driving a generator to produce electricity. The Atlantic's vital currents could collapse. Scientists ... (2) The warm currents heat up the surrounding air and land, helping to create temperate weather over Western Europe. (3) The surface waters become cooler and denser as they near the Arctic, driving... 6A: Down to the Deep - The Ocean's Biological Pump Oceans and the Carbon Cycle Part A: Down to the Deep - The Ocean's Biological Pump. Oceans have a large capacity to absorb CO 2, thus reducing the amount of CO 2 in the atmosphere and bringing carbon atoms into the ocean system. Many CO 2 molecules that diffuse into sea surface waters diffuse back to the atmosphere on very short time scales. However, some of the carbon atoms from these ...
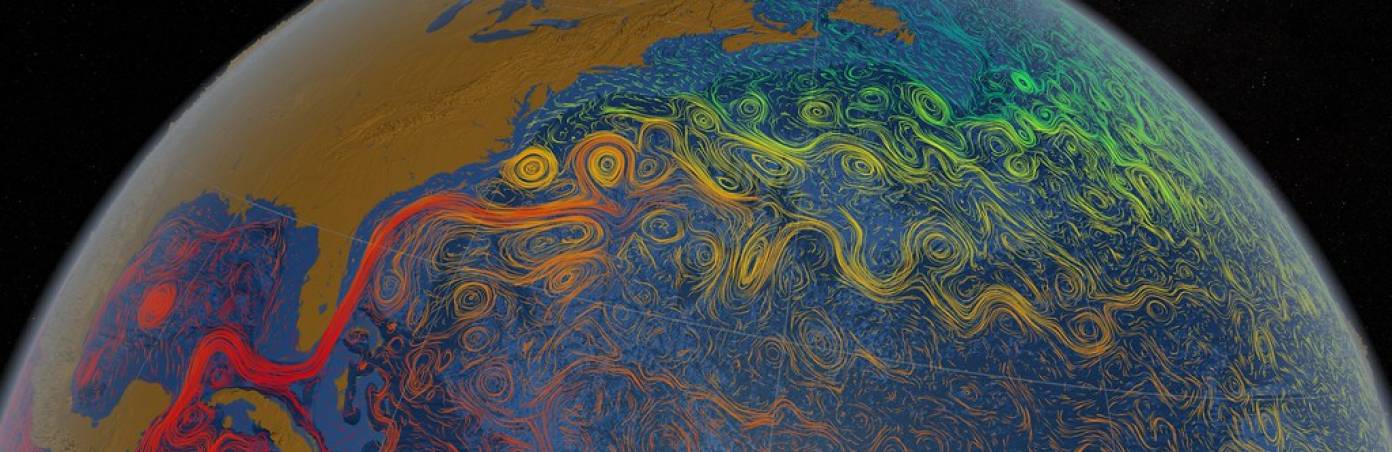
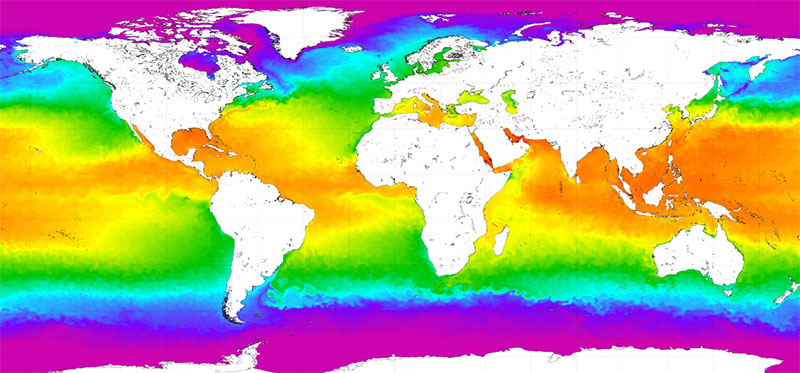
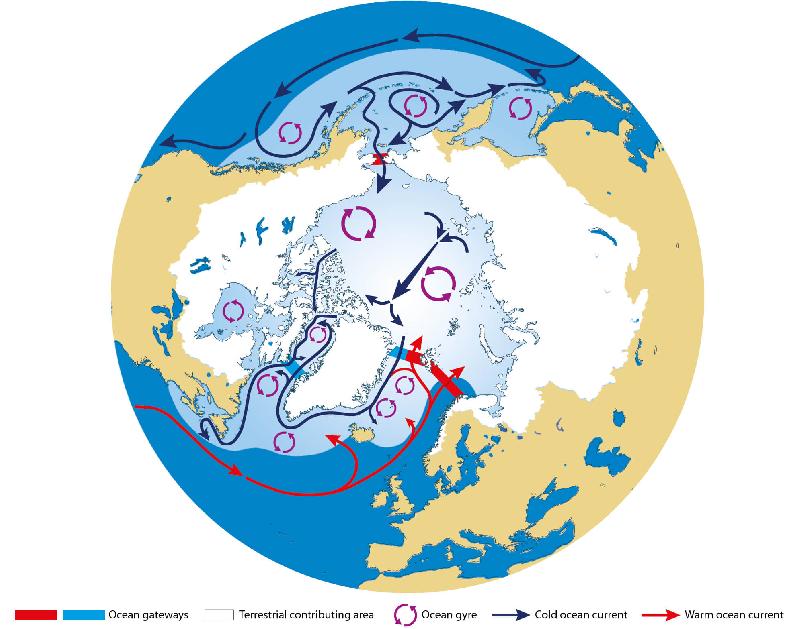
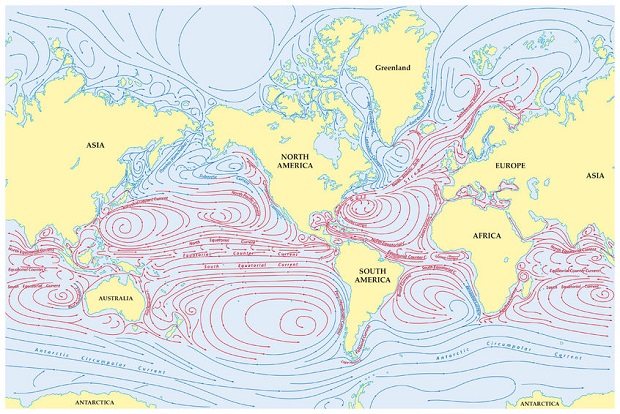
How do ocean currents work. how do ocean currents distribute heat - Lisbdnet.com Ocean currents act as conveyer belts of warm and cold water, sending heat toward the polar regions and helping tropical areas cool off, thus influencing both List of Ocean Currents of the World - Jagranjosh.com List of Ocean Currents of the World: Oceans are the lifeline of the Earth and humankind because it plays an important role in the Earth's climate and in global warming.Over half of the world's ... Ocean Currents | National Geographic Society What are Ocean Currents? - Definition & Types - Video ... This friction pushes the water along and forms a current moving in the same direction the wind is blowing. The current will continue in the direction of the wind until other factors - such as...
› movements-ocean-waves-tidesMovements of ocean water: Waves, Tides and Ocean Currents Nov 21, 2017 · Hence, ocean currents in the northern hemisphere move in a clockwise (towards right) direction and ocean currents in southern hemisphere moves in an anti-clockwise (towards left) direction (In the Indian Ocean due to the impact of the Asian monsoon, the currents in the northern hemisphere do not follow this pattern of movements all time). 3. › videolessons › climateClimate Zones & Ocean Currents Video For Kids | Middle School ... How do ocean and air currents help regulate the temperature of Earth? ANSWER. Ocean and air currents work together to distribute heat and moisture around Earth. Less-dense air and water rise; denser air and water sink. This creates a series of circulation systems that span the globe. Eddy Killing in the Ocean - Eos Wind destroys ocean eddies by applying stress to the ocean's surface and slowing eddies' spin to the point of extinguishing them. Because wind stress hinges on the difference between the speed and... One World Ocean - Activity - TeachEngineering Students learn about ocean currents and the difference between salt and fresh water by using colored ice cubes to see how cold and warm water mix and how this mixing causes currents. They also learn how fresh water floats on top of salt water, the difference between ocean and fresh, and how engineers are involved in the design of ocean water systems for human use.
12 Ocean Jobs for Marine Enthusiasts | Indeed.com They are responsible for testing and repairing parts, such as propellers, hulls, boat engines, navigation equipment, sails and masts. Additionally, they test and install refrigeration systems, electrical systems, steering gear, accessories and sanitation equipment. 3. Deckhand National average salary: $25.95 per hour Ocean Current System - That Influences Weather Patterns ... It moves heat from the Tropical region to the Northern hemisphere by transporting warm water masses northward at the ocean surface, and returning as a cool current southward at the bottom of the ocean. Part of Gulf Stream at risk as Atlantic Ocean currents ... The Atlantic Ocean's current system, an engine of the Northern Hemisphere's climate, could be weakening due to climate change, which could have severe consequences for the world's weather ... What is an Undertow? (with pictures) - All Things Nature When there is heavy wave action, the water may not be able to get out and as a result, it builds up and seeks a weak point in the breaking waves. When the water finds a weak point, it pushes out to sea, creating a rip current. As waves break on the shore, the water from the previous waves rush underneath them.
Ocean - Wikipedia The ocean (also the sea or the world ocean) is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of the surface of Earth and contains 97% of Earth's water. Another definition is "any of the large bodies of water into which the great ocean is divided". Separate names are used to identify five different areas of the ocean: Pacific (the largest), Atlantic, Indian, Southern (Antarctic), and ...
› media › ocean-currentsOcean Currents and Climate | National Geographic Society Mar 21, 2013 · Ocean currents are located at the ocean surface and in deep water below 300 meters (984 feet). They can move water horizontally and vertically and occur on both local and global scales. The ocean has an interconnected current, or circulation, system powered by wind, tides, the Earth’s rotation (Coriolis effect), the sun (solar energy), and ...
What Are Marine Heatwaves? Overview, Effects, and Mitigation One of the most common causes of marine heatwaves has to do with ocean currents. These currents contribute to marine heatwaves by allowing very warm water to accumulate in concentrated areas.
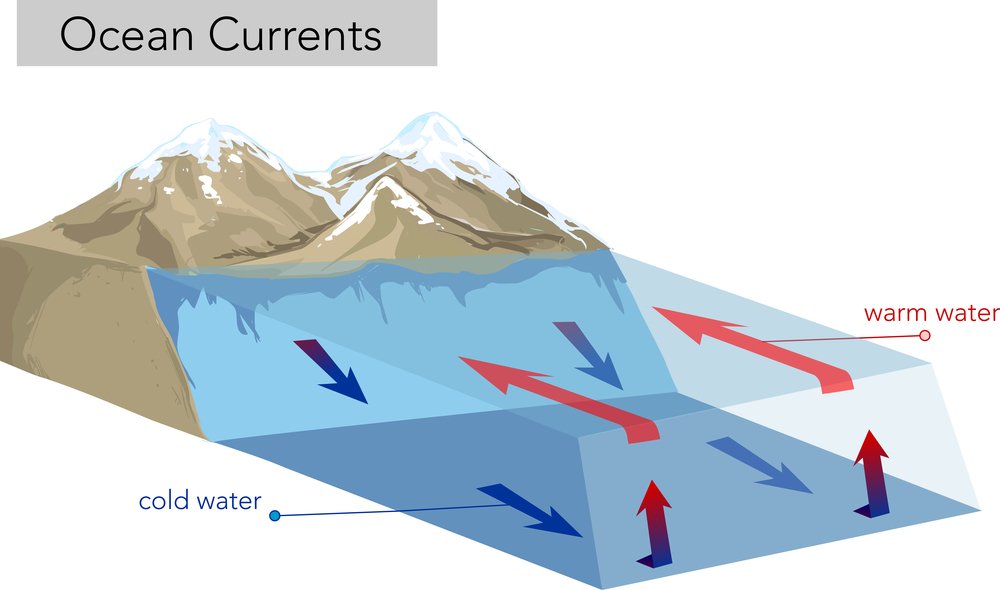
The Sun as a Source of Energy for Winds, Currents & the ... Warm waters rise just like warm air rises. So, as the warmer ocean waters begin to rise in a particular area, the cooler ocean waters from a different area will move in to replace the warmer ocean...
How Can We Use Ocean Energy to Generate Electricity ... Ocean currents are mainly formed by the rotation of the Earth, variations in the seabed, and the differences in the temperature and salinity (saltiness) of the waters in the sea. Some ocean currents are very strong and the major currents even have specific names. Some currents carry warm, or even hot water; others carry cold water.
manoa.hawaii.edu › ocean-surface-currentsOcean Surface Currents | manoa.hawaii.edu/ExploringOurFluidEarth Ocean currents are produced by friction created by wind blowing over the water surface. However, the direction and speed of water currents do not match those of the wind currents above them. A 20 km/h eastward wind does not produce a 20 km/h eastward current. Ocean currents are much slower than winds due to friction.
Wave Energy Pros and Cons - Solar Reviews Ocean waves exert tremendous amounts of power - power which can be utilized as a renewable resource known as wave energy, or tidal energy. The United States has the potential to generate 2.64 trillion kilowatt-hours of ocean energy - or more than half of the energy generated within the U.S. in 2020.. If we had the potential to generate more than half of the U.S. electricity from waves, what is ...
Protecting Our Oceans from Pollution | US EPA EPA's Ocean Dumping Management Program plays a primary role in protecting and preserving our ocean and coastal resources. EPA regularly evaluates ocean disposal inquiries from the public and provides technical support to other agencies to ensure that ocean dumping is appropriately regulated and safeguards human health and the environment.
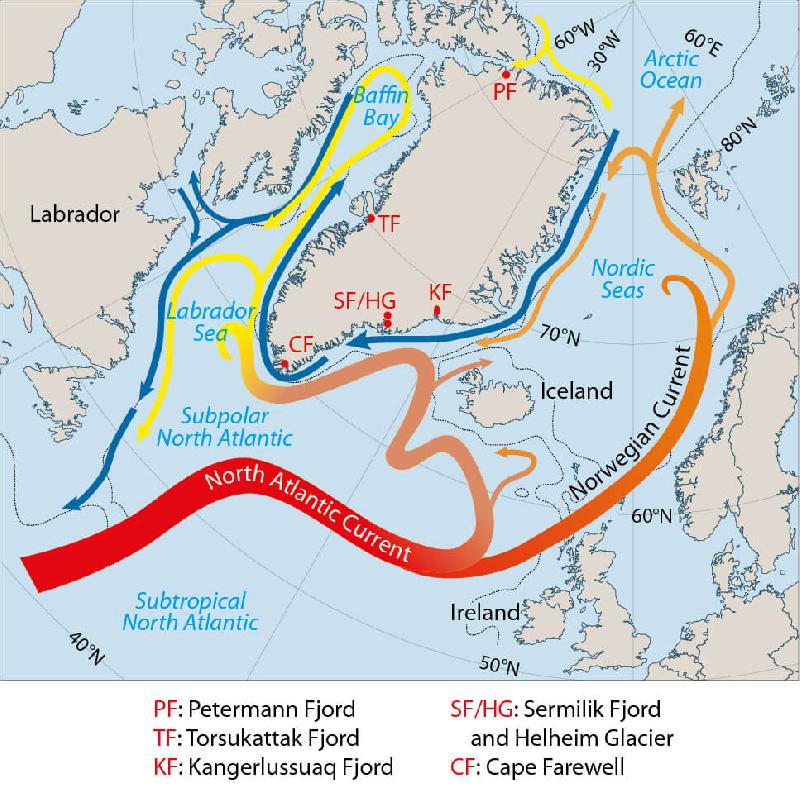
Ocean Currents - Shortcut method by to learn faster ... A cold current from the Arctic Ocean called Labrador Current, which flows along the eastern coast of Canada, meets the warm Gulf Stream near the northeast corner of the U.S.A. The confluence of these two currents, one cold and the other warm, produce fog around the region and makes it the most important fishing ground in the world.
Changing ocean currents are driving extreme winter weather ... Changing ocean currents are driving extreme winter weather. Slower ocean circulation as the result of climate change could intensify extreme cold weather in the U.S., according to new research ...
marine-conservation.org › why-protect-the-oceanWhy Protect Oceans? - Marine Conservation Institute Why Protect the Ocean? The ocean generates over half of the oxygen we breathe. Phytoplankton, tiny marine plants that live on the ocean’s surface, photosynthesize and produce an estimated 50-80% of Earth’s oxygen. The ocean contains more than 97% of the world’s water. The ocean covers approximately 71% of the planet and contains over one billion…
large.stanford.edu › courses › 2014Ocean Current Energy: Underwater Turbines Ocean currents flow in complex patterns and pathways and are affected by several elements such as wind, temperature, topography of the ocean floor, the earth's rotation and water salinity. Most ocean currents are driven by wind and solar heating of surface waters, while some currents result from density and salinity variations of the water column.
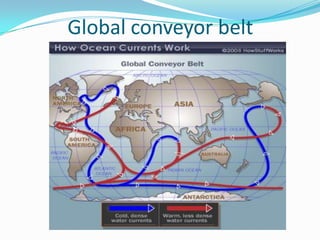
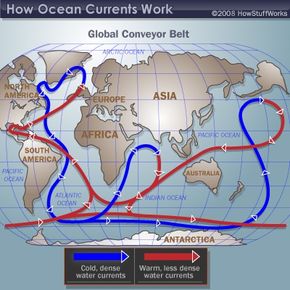
3A: Planetary Circulation Patterns - Climate and the Biosphere Ocean currents transport the remainder of the heat. These currents include both surface, or wind-driven currents, and thermohaline (thermo=heat; haline=salt) or density currents. A simple schematic of these currents is pictured at left. It is estimated that the water in these currents may take a thousand or more years to circulate the globe!
where do cold ocean currents originate - Lisbdnet.com 2 Where do these ocean currents originate from? 3 Where do cold currents travel from? 4 Which is cold ocean current? 5 Why do warm ocean currents begin at the equator? 6 Where does the Benguela Current come from? 7 Where is the Labrador Current located? 8 What warm current keeps Australian? 9 Which is an example of cold current? 10 Is the West ...
What does an Ocean Engineer do? (with pictures) Working with a team of other marine specialists, an ocean engineer creates blueprints and schematics for new equipment and vehicles using computer-aided design ( CAD) software. He or she puts designs through simulated computer tests to determine their effectiveness, and then oversees the construction of models and prototypes.
Ocean thermal energy conversion - U.S. Energy Information ... Ocean thermal energy conversion (OTEC) is a process or technology for producing energy by harnessing the temperature differences (thermal gradients) between ocean surface waters and deep ocean waters. Energy from the sun heats the surface water of the ocean. In tropical regions, surface water can be much warmer than deep water.
Atlantic Ocean Currents Weakening, Near Verge of Collapse ... The Pulse of the Ocean The Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation, or AMOC, plays an essential role in regulating ocean temperatures. It is composed of a network of currents branching throughout the Atlantic Ocean like veins and arteries — some scientists compare it to the ocean's pulse. The AMOC works like a perpetually turning conveyor belt.
6A: Down to the Deep - The Ocean's Biological Pump Oceans and the Carbon Cycle Part A: Down to the Deep - The Ocean's Biological Pump. Oceans have a large capacity to absorb CO 2, thus reducing the amount of CO 2 in the atmosphere and bringing carbon atoms into the ocean system. Many CO 2 molecules that diffuse into sea surface waters diffuse back to the atmosphere on very short time scales. However, some of the carbon atoms from these ...
The Atlantic's vital currents could collapse. Scientists ... (2) The warm currents heat up the surrounding air and land, helping to create temperate weather over Western Europe. (3) The surface waters become cooler and denser as they near the Arctic, driving...
How does OTEC work? (ocean thermal energy conversion ... How does it work? First, the pipe flows through a heat exchanger fixed in the hot surface waters of the ocean, which makes the ammonia boil and vaporize. The heated ammonia vapor expands and blows through a turbine, which extracts some of its energy, driving a generator to produce electricity.












/GettyImages-761606665-5a599d45e258f80037f13b4c.jpg)
















0 Response to "43 how do ocean currents work"
Post a Comment